Why Choose a Switching Power Supply for Your Electronics?
In today's fast-paced electronics landscape, the need for efficient power supply solutions is paramount. A Switching Power Supply stands out for its versatility and effectiveness. It regulates voltage output while minimizing energy loss, making it ideal for various applications.
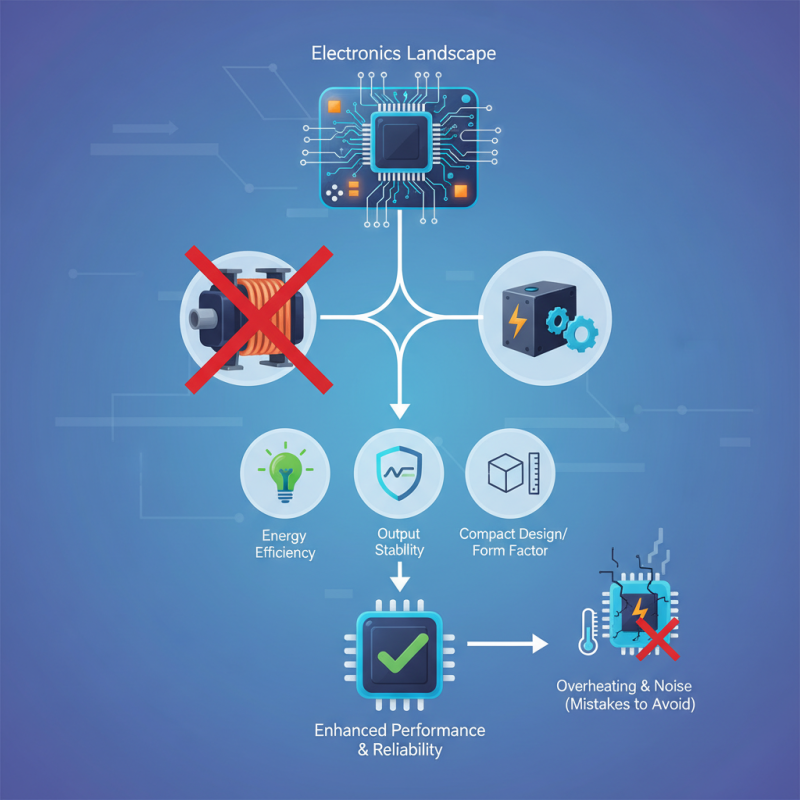
Switching Power Supply units excel in compact designs. They replace larger, bulkier options, saving precious space in your devices. However, not all units are created equal. Some may experience overheating or noise interference, which can affect performance.
Choosing a Switching Power Supply requires careful consideration. Evaluate energy efficiency, output stability, and form factor. Mistakes can lead to failures in your electronic projects. By understanding these factors, you can make informed decisions that enhance your devices' performance and reliability.
Understanding the Basics of Switching Power Supplies
Switching power supplies are essential for modern electronics. They convert electrical power efficiently, providing the necessary voltage for various devices. Understanding how they work can enhance your project design. Unlike traditional linear power supplies, switching models regulate voltage through a high-frequency switching circuit. This allows for smaller, lighter designs that generate less heat, which is crucial for compact electronics.
**Tip:** Choose the right output voltage for your device. A mismatch can lead to poor performance or damage.
These supplies can operate under many conditions, but they are not without flaws. Noise and electromagnetic interference are common issues. Filtering circuits can minimize these effects, but they require careful design and testing. Keep in mind that not all switching supplies are created equal.
**Tip:** Perform a load test before full implementation. This helps identify issues early on, saving time and resources.
Designing with switching power supplies is a balance of performance and practicality. Understanding their behavior can lead to better electronics. However, it’s essential to address potential weaknesses in your design for optimal results.
Advantages of Using Switching Power Supplies in Electronics
Switching power supplies have gained significant popularity in modern electronics. One compelling advantage is their efficiency. Reports indicate that switching power supplies can achieve efficiencies of up to 90% or more. This means less energy waste and lower electricity costs. In contrast, linear power supplies often operate with only 30% to 50% efficiency. This stark difference highlights why more designers opt for switching technologies.
Another notable benefit lies in their compact size. Switching power supplies are typically smaller and lighter than their linear counterparts. This makes them ideal for portable devices, where space is at a premium. For instance, a typical switching supply can be 50% smaller than a linear one, without compromising performance. However, it's crucial to acknowledge that the complexity of switching designs can sometimes lead to noise interference, which can be a challenge in sensitive applications.
Thermal performance also plays a crucial role in the decision-making process. Switching power supplies generate less heat due to their higher efficiency. This can enhance the lifespan of electronic components. A study suggested that devices running cooler tend to have a longer operational life. However, proper thermal management is still essential, as inadequate cooling could negate these advantages. Balancing efficiency, size, and heat management requires a thoughtful approach from engineers.
Applications of Switching Power Supplies in Modern Devices
Switching power supplies have become indispensable in modern electronics. They are found in a diverse range of devices such as smartphones, laptops, and home appliances. According to a report from ResearchAndMarkets, the global switching power supply market is projected to reach $36 billion by 2025. This growth highlights their increasing significance in our daily lives.
The applications of switching power supplies are quite varied. In telecommunications, they ensure stable performance under fluctuating power conditions. Moreover, in consumer electronics, they allow devices to be lightweight and compact. An efficiency rating of over 90% is common in these power supplies, meaning less energy is wasted. However, there remain concerns regarding electromagnetic interference. This can impact sensitive equipment in medical and industrial sectors.
In the automotive industry, switching power supplies are crucial for electric vehicle charging systems. They must adapt to changing energy requirements, which poses design challenges. It's vital to create solutions that enhance efficiency while minimizing noise. Continuous improvements are necessary for better reliability and performance across various applications.
Comparison: Switching vs Linear Power Supplies
When considering power supply options, understanding the differences between switching and linear power supplies is essential. Switching power supplies are often preferred due to their efficiency. They can achieve efficiencies greater than 90%, as highlighted in a 2022 industry report by the International Energy Agency. In contrast, linear power supplies often operate at 60% to 80% efficiency, leading to higher heat generation and wasted energy.
Switching power supplies use a high-frequency switching mechanism to convert voltage. This allows for smaller components, resulting in compact designs. They also react quickly to load changes. However, switching supplies can introduce noise into circuits. This can be problematic for sensitive electronics. Meanwhile, linear power supplies deliver clean power with minimal ripple. They excel in low-noise applications, but at the cost of size and weight.
Cost is another critical factor. A report from the Power Supply Manufacturers Association noted that switching power supplies are generally cheaper to produce due to their high efficiency and compactness. However, linear supplies are often seen as more stable, albeit pricier. Developers must weigh these aspects carefully when designing circuits for their applications. Each option has trade-offs worth considering.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Switching Power Supply
When selecting a switching power supply, several crucial factors come into play. One key aspect is efficiency. Recent industry reports show that a high-quality switching power supply can achieve over 90% efficiency at full load. This translates to less heat generated and lower energy bills. However, efficiency can vary significantly among models, making careful comparison essential.
Another important consideration is the output voltage range. A flexible output allows for compatibility with various electronic devices. Many applications require specific voltage levels, and not all power supplies can accommodate those needs. In some cases, using an incompatible supply could lead to device malfunction or reduced performance. Additionally, the size and weight of the power supply also matter. Compact models save space but may sacrifice cooling and durability.
Finally, the reliability of a power supply cannot be overlooked. Data indicates that poor quality supplies can fail prematurely, leading to costly downtimes. It’s estimated that 30% of electronic device failures are due to power supply issues. Therefore, investing in a reliable switching power supply is crucial for long-term performance.
Performance Comparison of Switching Power Supplies
This chart compares the performance metrics of a standard switching power supply against a high-efficiency switching power supply. The parameters evaluated include efficiency, size, cost, noise level, and weight. Understanding these characteristics helps in making an informed decision when choosing the right power supply for your electronics.